Colloquial arts and Indian Arts
Colloquial Art and Indian Art
Art, as a medium of expression and visual beauty, predates verbal communication, serving as humanity's earliest form of self-expression. Even before the advent of language, humans turned to art to convey emotions, ideas, and experiences. With the emergence of verbal communication, art evolved into a decorative and aesthetic expression, transcending mere utility to become a defining aspect of human identity. This transformation marked a shift in the purpose of art, from necessity to cultural emblem. As civilizations flourished, so too did art, blossoming into an independent cult of creativity and expression. Across the globe, including in India, this development of art has been witnessed and celebrated, reflecting the diverse and rich tapestry of human culture.
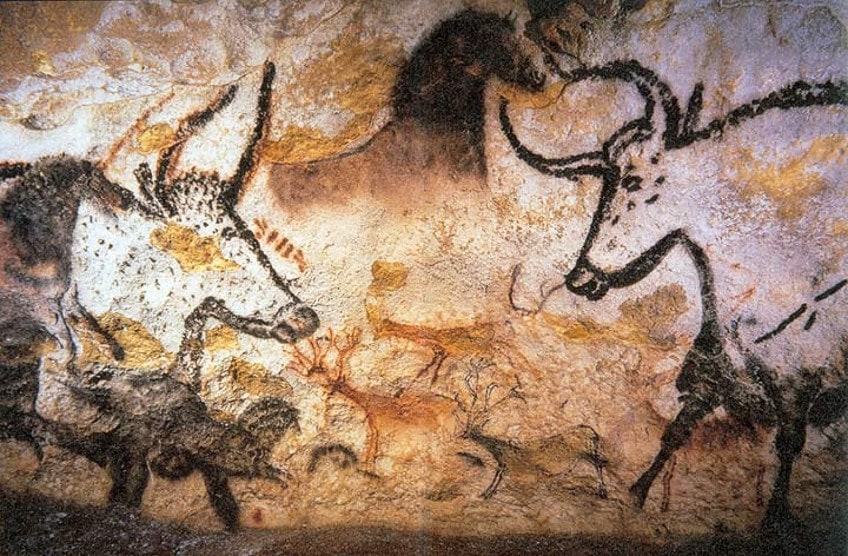
Pre-historic art
Colloquial art styles span the globe, reflecting the unique cultural identities and histories of diverse civilizations. In the Andean realm of the Incas, intricate textiles and vibrant ceramics showcased their advanced weaving and pottery techniques, often depicting symbolic motifs of nature and mythology. Egyptian art, characterized by its monumental sculptures, intricate hieroglyphics, and stunning tomb paintings, served both religious and funerary purposes, immortalizing pharaohs and deities alike. The Romans and Greeks left behind a legacy of classical art, with their emphasis on idealized human forms and architectural grandeur, influencing art for centuries to come. Beyond the Euro-centric lens, non-European civilizations such as those in Africa, South Asia, and the Americas produced art that was deeply rooted in cultural traditions and spiritual beliefs. African art, with its emphasis on abstract forms and ritualistic masks, conveyed a profound connection to the natural and spiritual worlds. South Asian art, spanning from the intricate carvings of Hindu temples to the delicate brushwork of Mughal miniatures, showcased a rich tapestry of influences from Buddhism, Islam, and indigenous traditions. The diverse tribes of the Americas expressed themselves through a myriad of mediums, from the colorful textiles of the Andean peoples to the intricate wood carvings of Native American tribes, each reflecting their unique cultural heritage and connection to the land. These colloquial art styles stand as testament to the richness and diversity of human creativity across the globe.
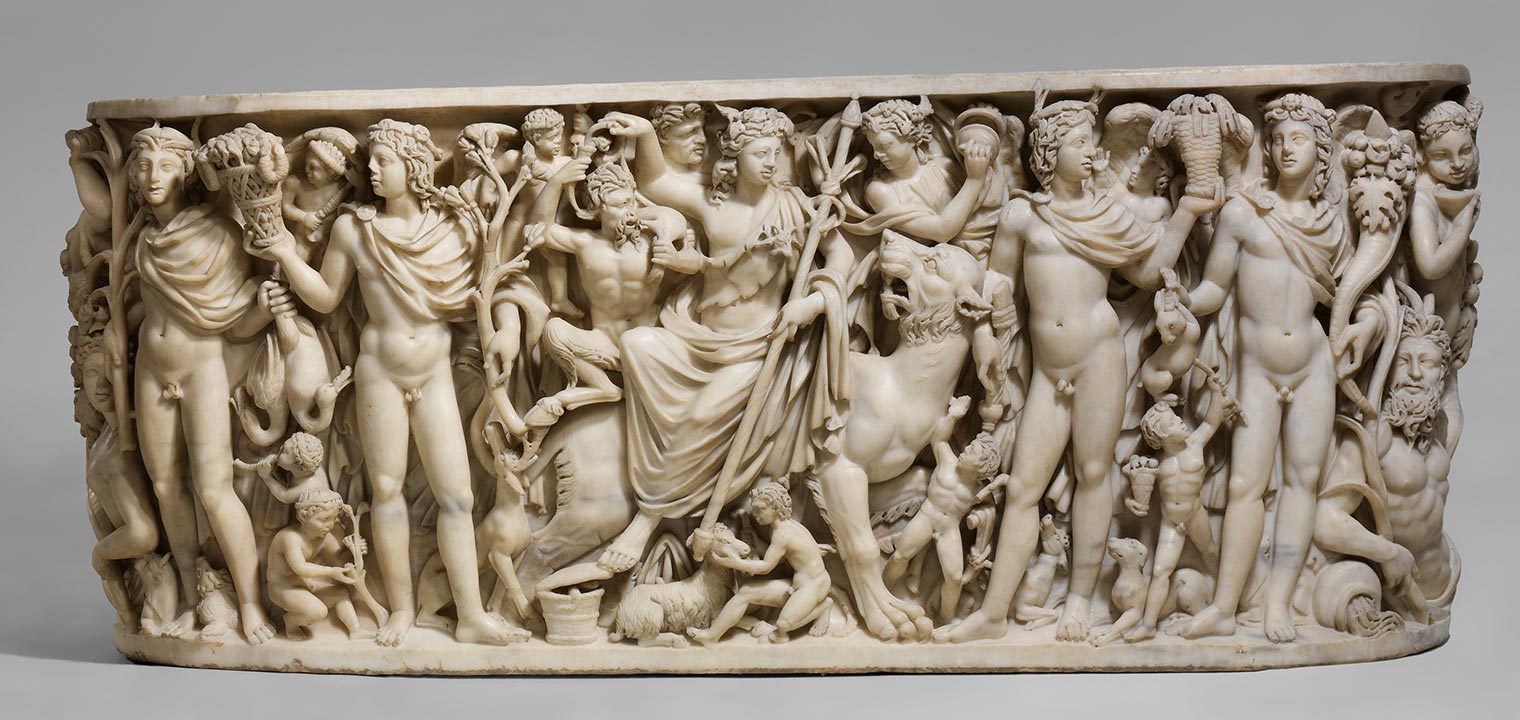
Western Classic Art
Western classical art has long been synonymous with the pursuit of realism, a tradition that traces its roots back to ancient Greece. From the marble sculptures of the Parthenon to the masterful paintings of the Renaissance, artists have endeavored to capture the essence of reality with remarkable precision. Inspired by the ideals of beauty and harmony espoused by Greek philosophers such as Plato and Aristotle, ancient Greek artists sought to depict the human form with unparalleled accuracy, striving for anatomical perfection and emotional depth in their sculptures and paintings. This commitment to realism continued to flourish throughout the Renaissance period, as artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo pushed the boundaries of artistic expression with their meticulous attention to detail and mastery of perspective. The legacy of Greek realism endures in the Western artistic tradition, serving as a cornerstone for generations of artists who continue to explore the complexities of the human experience through the lens of realism.
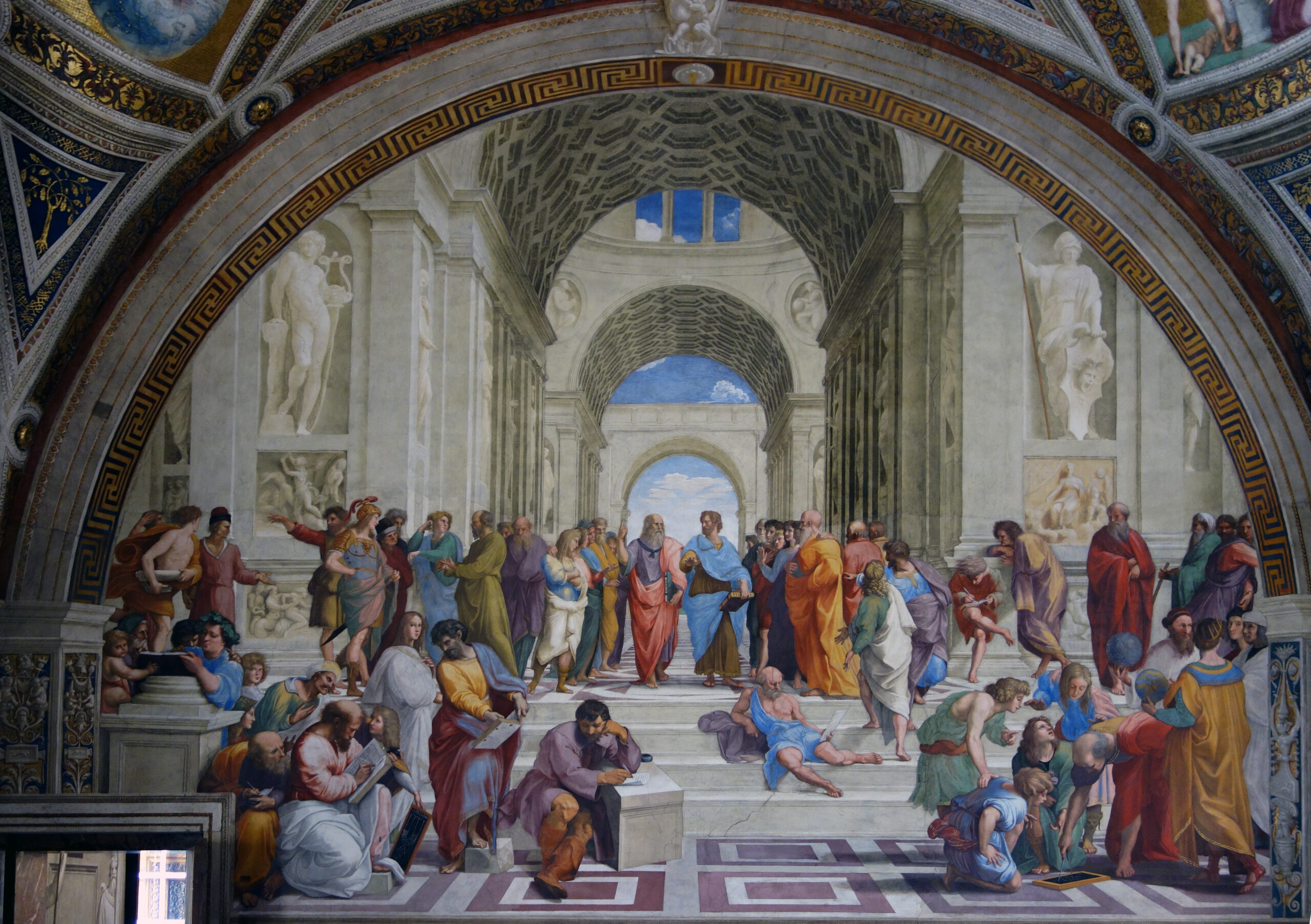
Renaissance Art
The Renaissance, a period of cultural and artistic rebirth spanning roughly from the 14th to the 17th century, marked a pivotal moment in Western history. Emerging from the shadows of the medieval era, the Renaissance saw a resurgence of interest in the classical ideals of ancient Greece and Rome, igniting a fervent pursuit of knowledge, beauty, and innovation. This period witnessed a flourishing of artistic achievements, as painters, sculptors, architects, and scholars sought to break free from the constraints of tradition and explore new avenues of creativity. The Renaissance artists, inspired by the humanist philosophy that celebrated the individual and the human experience, revolutionized the way art was conceived and executed. Masters like Leonardo-da-Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael ushered in a golden age of art, producing timeless masterpieces that continue to captivate and inspire audiences to this day. The Renaissance was not only a cultural rebirth but also a period of profound intellectual and scientific advancements, laying the groundwork for the modern world and forever shaping the course of Western civilization.
Indian Arts
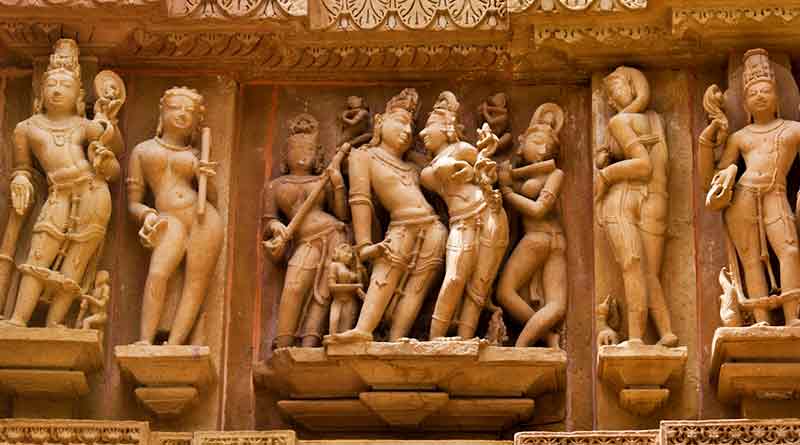
Indian art has been profoundly shaped by the rich tapestry of Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist architectural scriptures and works, as well as the principles of Vastu Shastra. Rooted in ancient texts and traditions, Indian artistry encompasses a vast array of styles and techniques, from intricate sculptures to elaborate temple architecture. Unlike Western art, which often prioritizes hyper-realism, Indian art emphasizes symbolism and spiritual significance, drawing upon the principles of samudrika lakshanas (physical characteristics) and the intricate details of anatomy as prescribed in ancient texts. Sculptures, for example, are crafted with meticulous attention to anatomical detail, yet they often transcend realism to convey deeper spiritual meanings. Symmetry and ornamentation play a central role in Indian art, offering artists a wide scope for creativity while maintaining conceptual appeal. This emphasis on symmetry and ornamentation, combined with a reverence for tradition and spirituality, has resulted in a distinctive and timeless aesthetic that continues to inspire and captivate audiences around the world.
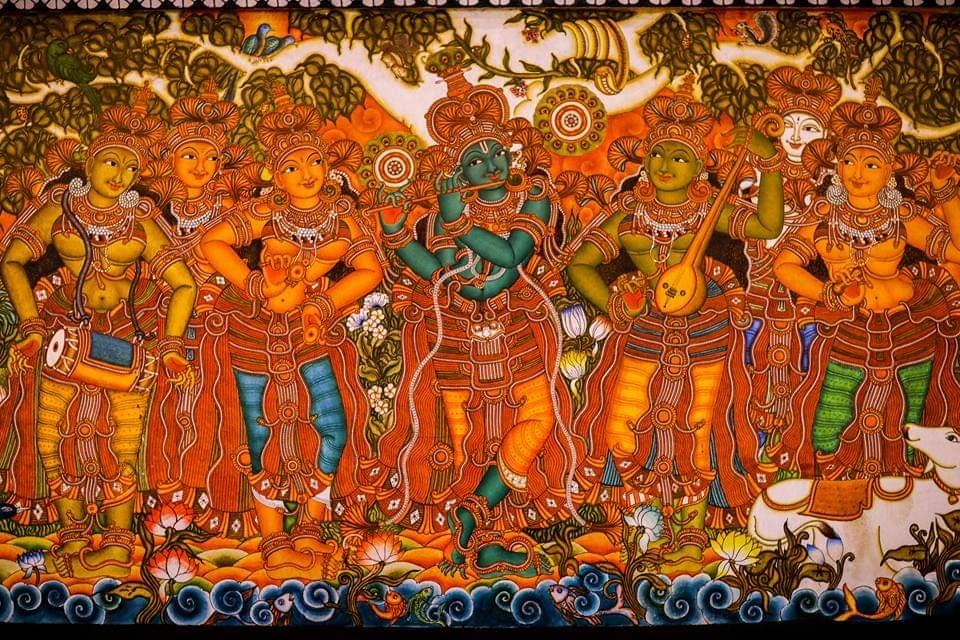
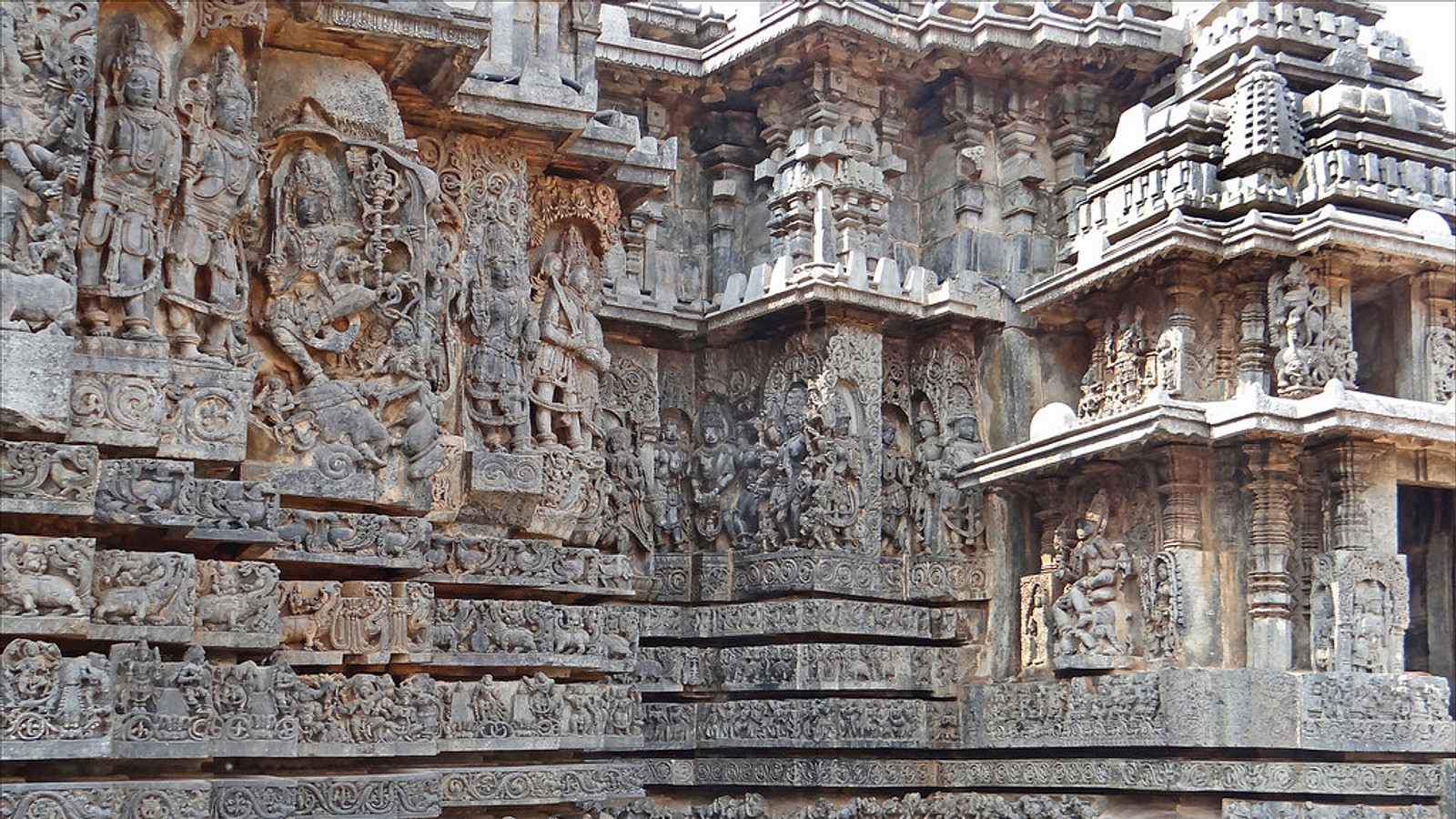
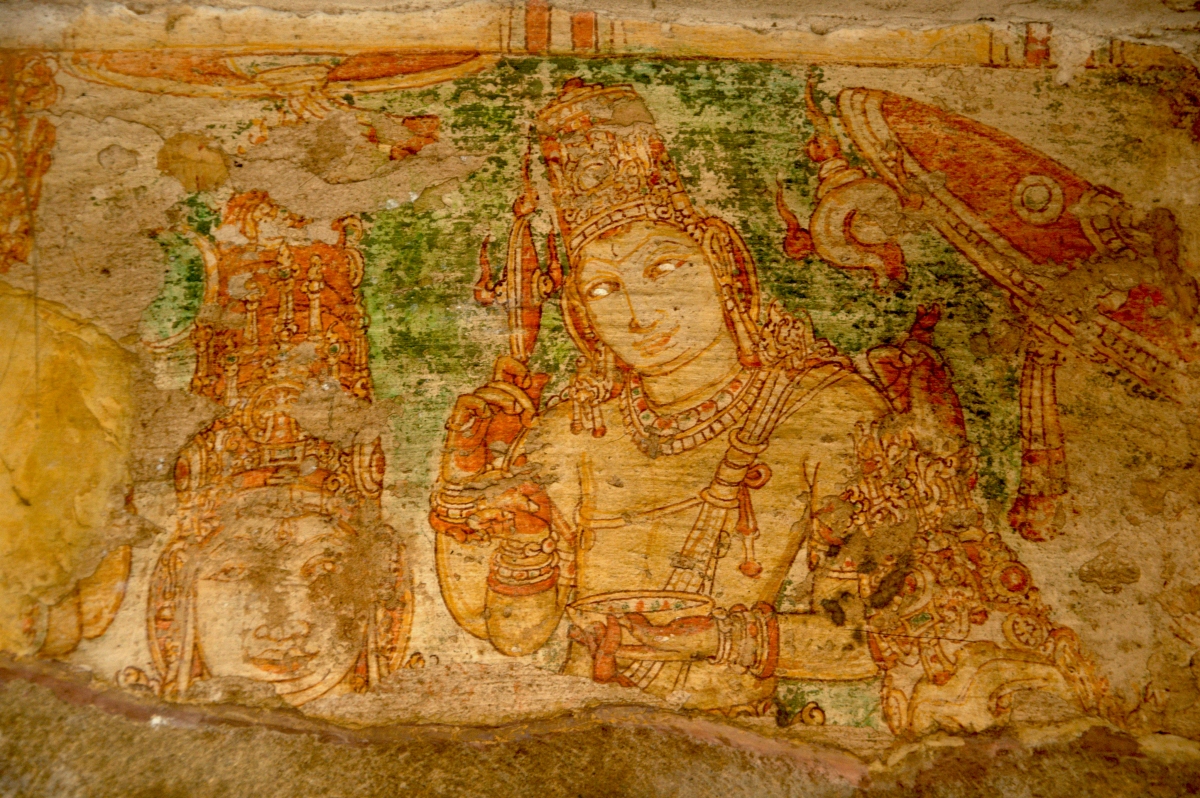
Ajanta Ellora Art styles
Indian art boasts a myriad of styles, each with its own distinct characteristics and cultural significance.
- Kerala Mural art, originating from the southern state of Kerala, is known for its vibrant colors and intricate detailing, often depicting mythological themes on temple walls.
- Hoysala sculptures, prevalent in Karnataka, feature highly ornate stone carvings adorned with intricate motifs and sculptures of deities.
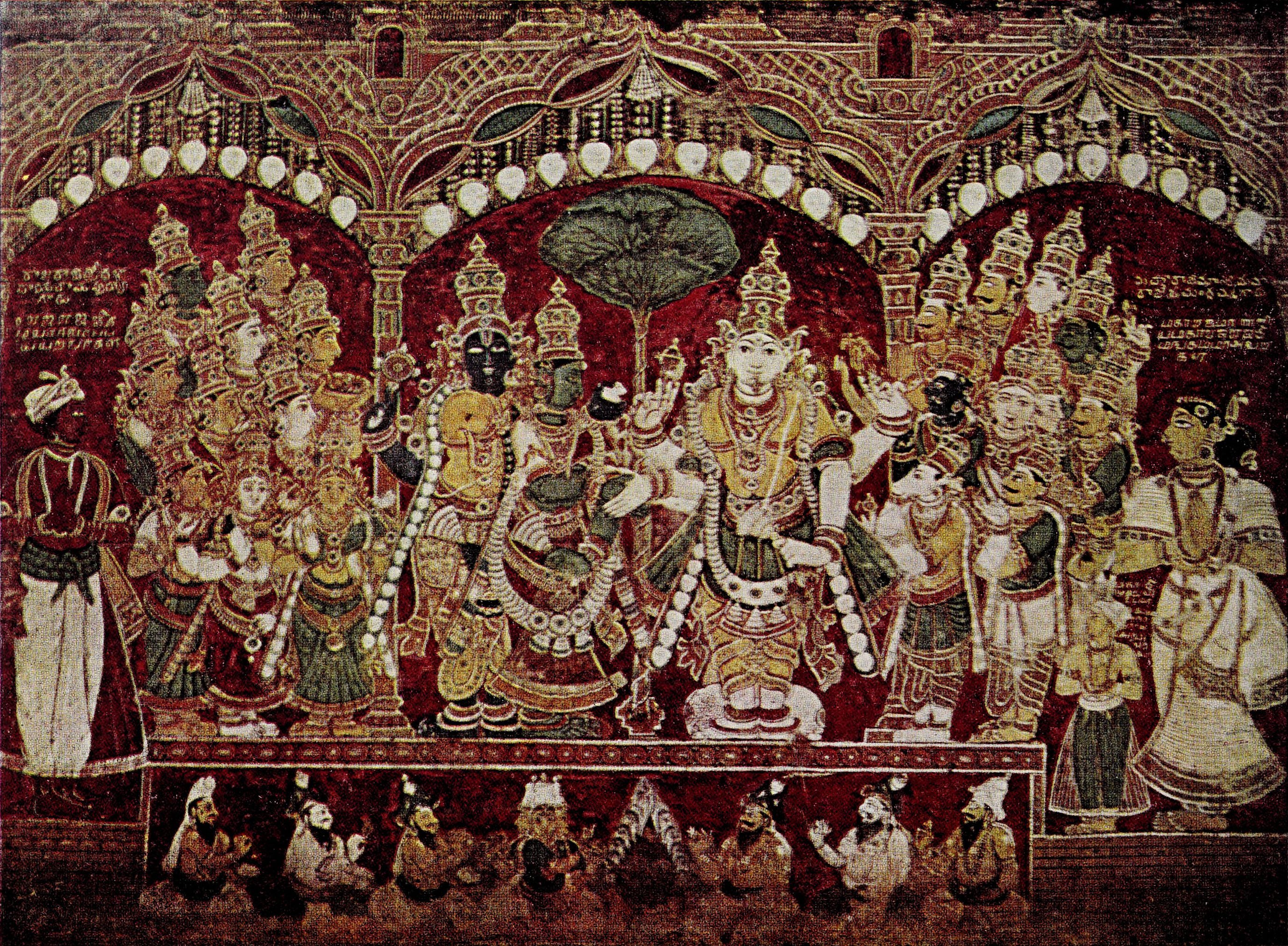
- Chola and Pallava art, originating from Tamil Nadu, are renowned for their majestic temple architecture and intricate stone carvings, showcasing exquisite craftsmanship and religious devotion.
- Vijayanagara art, from the Vijayanagara Empire in South India, is characterized by grandiose temple complexes adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures.
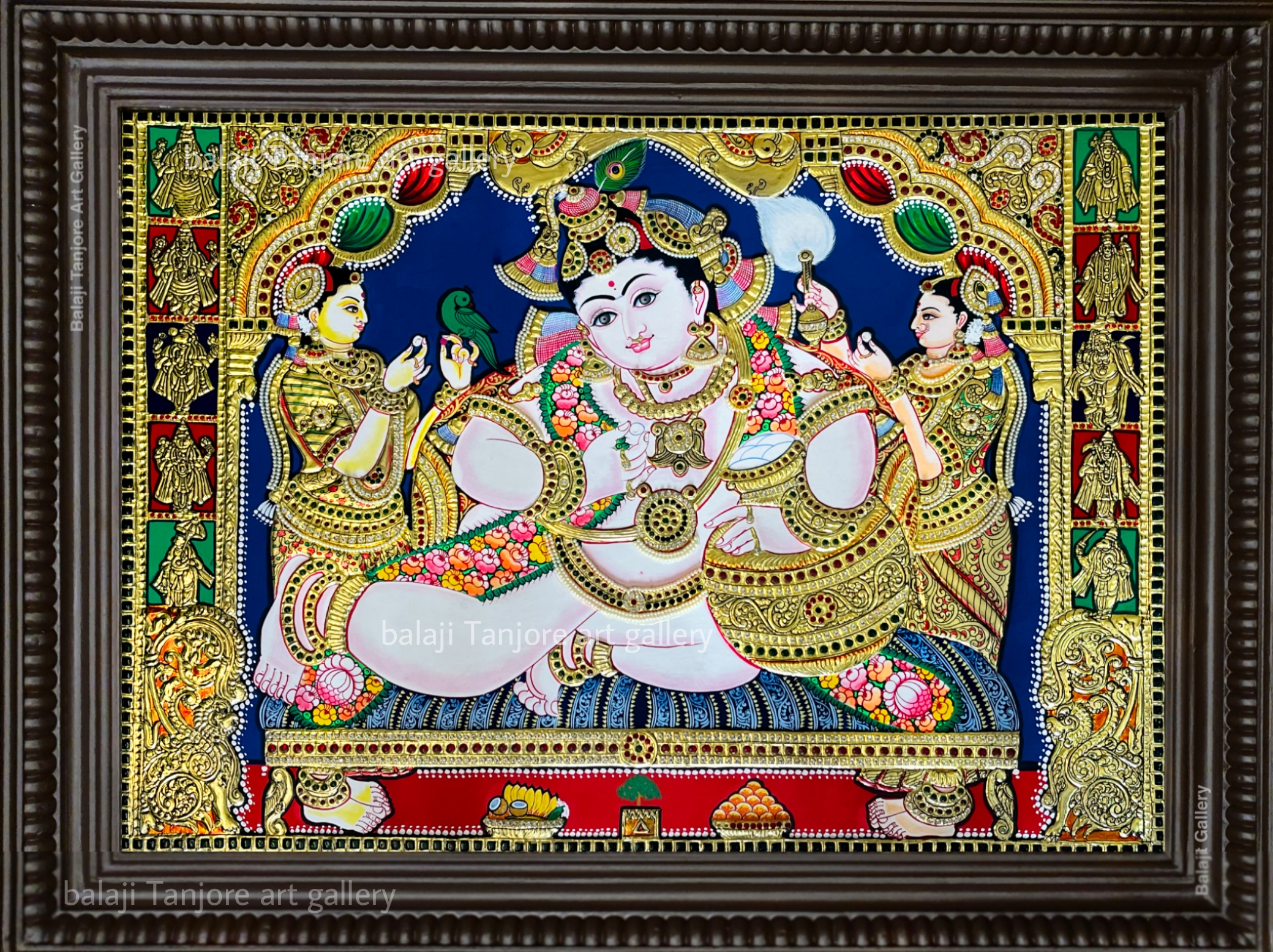
- Tanjore paintings, originating from Tamil Nadu, are known for their rich colors, gold leaf embellishments, and depictions of gods and goddesses in a highly stylized manner.
- Pattachitra, a traditional art form from Odisha and West Bengal, features intricate paintings on cloth depicting mythological narratives and daily life scenes.
- Newari paintings, prevalent in Nepal, are characterized by intricate details and vibrant colors, often depicting religious themes and cultural motifs.
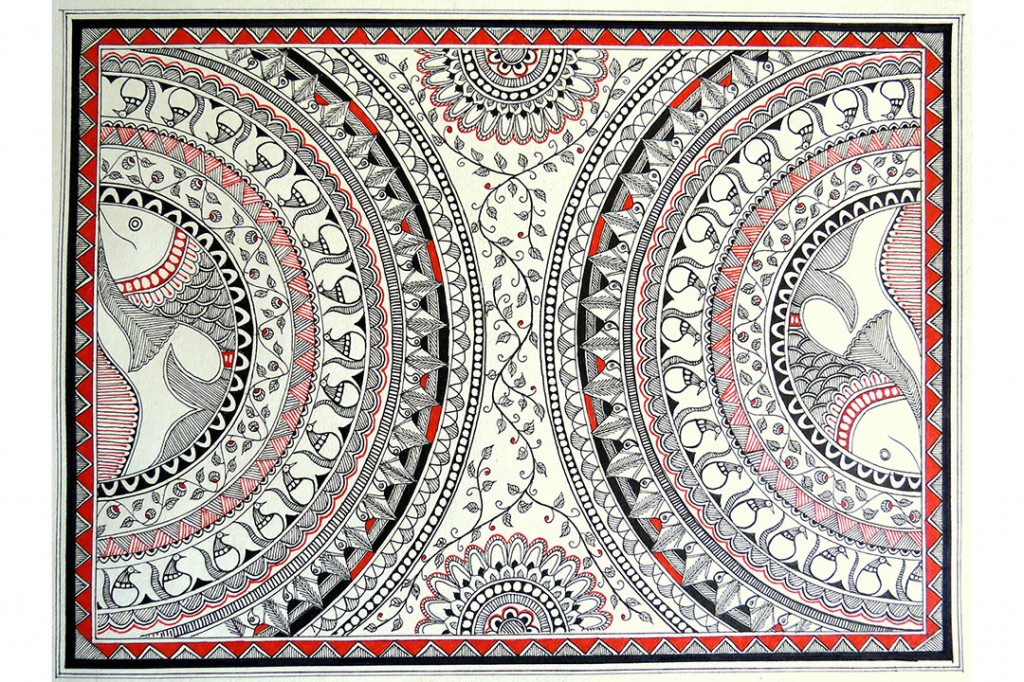
- Madhubani paintings, originating from Bihar, are known for their intricate patterns and vibrant colors, depicting scenes from mythology and nature.
- Rajasthani miniature paintings, originating from the desert state of Rajasthan, feature intricate brushwork and elaborate detailing, often depicting royal court scenes and mythological tales.
- Gupta sculpture art, from the Gupta Empire, is celebrated for its elegant forms and serene expressions, showcasing the pinnacle of classical Indian sculpture. Each of these styles represents a unique facet of India's rich artistic heritage, spanning centuries of cultural evolution and creative expression.












Very interesting and informative
ReplyDeleteచారిత్రక విజ్ఞాన కాంతుల చక్కని వివరణ
ReplyDeleteGood to know
ReplyDeleteGood to know about our ancient culture and sculpture.. great blog!
ReplyDelete